Product Description
Agricultural farm machinery spreader Gearbox For Fertilizer Sprayers
1. Product Description
| MODEL |
INPUT DATA | OUTPUT DATA | |||||
| Ratio | Maximum Rpm | KW | HP-CV | N.M | N.M | R.P.M | |
| AC78845A/B | 1:1.93 | 800 | 30 | 40 | 358 | 185 | 1544 |
| RC | 1:1.93 | 800 | 30 | 40 | 358 | 185 | 1544 |
| RC5/BB60X | 1:1.69 | 800 | 37 | 50 | 440 | 260 | 1352 |
| AC78846A/B | 1:1.93 | 540 | 55 | 75 | 972 | 504 | 1042 |
| 612619 | 1:1.93 | 540 | 74 | 100 | 1308 | 678 | 1042 |
| 612666 | 1:1.46 | 540 | 74 | 100 | 1308 | 896 | 680 |
| BB84X | 1:1.26 | 540 | 67 | 90 | 1184 | 940 | 680 |
| RC81-000-01 | 1:1.923 | 540 | 74 | 100 | 1308 | 680 | 1038 |
| RC81-000-02 | 1:1.46 | 540 | 74 | 100 | 1308 | 896 | 788 |
| 75356-192 | 1:1.92 | 540 | 97 | 130 | 1715 | 893 | 1037 |
| 75356-146 | 1:1.46 | 540 | 97 | 130 | 1715 | 1175 | 788 |
| 74823-19 | 1:1.87 | 540 | 97 | 130 | 1715 | 918 | 1009 |
| 74823-14 | 1:1.39 | 540 | 97 | 130 | 1715 | 1235 | 750 |
| GT40U.B | 3:1 | 540 | 44 | 60 | 778 | 2334 | 180 |
| SF-100 | 1:1 | 540 | 15 | 20 | 265 | 265 | 540 |
| MCT-100A1 | 7.5:1 | 540 | 29.5 | 40 | 521 | 3912 | 72 |
| MCT-100A2 | 22.5:1 | 540 | 29.5 | 40 | 521 | 11738 | 24 |
| DCR1-0000 | 2.4:1 | 540 | 37 | 50 | 654 | 1570 | 225 |
2. More Products
3. The Drawing Of Gear Box
4. Production and Packing
5.Shipping
6.Our Company
HangZhou CZPT Tech.Machinery Co.,Ltd was founded in 2003. It is located at HangZhou County, HangZhou City, closed to 204 National Road.Our main products: 1. all kinds of drive shaft 2.all kinds of gera box 3. Farm machinery: IMT500 inorganic fertilizer spreader, HMT05S organic fertilizer spreader, 3M rotovator , 3M wet-paddy field rotary, King 185 deep cultviating machine and so on. 4.The machinery parts: many kinds of Gear, Shaft, Flang, ,Gear box, Laser parts, Stamping parts and so on.
7. FAQ
1. Q: Are your products forged or cast?
A: All of our products are forged.
2. Q: What’s your MOQ?
A: 20 PCS for each type. We accept the sample order.
3. Q: What’s the horse power of the pto shaft are available?
A: We provide a full range of pto shaft, ranging from 16HP-200HP.
4. Q: How many splined specification do you have ?
A: We produce 1 1/8″-Z6, 1 3/8″-Z6, 1 3/4″-Z6, 1 3/8″- Z21, 1 3/4″-Z20, 8X42X48X8 and 8X32X38X6 splines.
5. Q: How about the warranty?
A: We guarantee 1 year warranty. With quality problems, we will send you the new products for free within next shipment.
6. Q: What’s your payment terms?
A: T/T, L/C, D/A, D/P….
7. Q: What is the delivery time?
A: 40 days after receiving your advanced deposit.
|
US $50-110 / Piece | |
30 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Function: | Distribution Power, Clutch, Change Drive Torque, Change Drive Direction, Speed Changing, Speed Reduction, Speed Increase |
| Layout: | Cycloidal |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Horizontal Type |
| Step: | Four-Step |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| MODEL |
INPUT DATA | OUTPUT DATA | |||||
| Ratio | Maximum Rpm | KW | HP-CV | N.M | N.M | R.P.M | |
| AC78845A/B | 1:1.93 | 800 | 30 | 40 | 358 | 185 | 1544 |
| RC | 1:1.93 | 800 | 30 | 40 | 358 | 185 | 1544 |
| RC5/BB60X | 1:1.69 | 800 | 37 | 50 | 440 | 260 | 1352 |
| AC78846A/B | 1:1.93 | 540 | 55 | 75 | 972 | 504 | 1042 |
| 612619 | 1:1.93 | 540 | 74 | 100 | 1308 | 678 | 1042 |
| 612666 | 1:1.46 | 540 | 74 | 100 | 1308 | 896 | 680 |
| BB84X | 1:1.26 | 540 | 67 | 90 | 1184 | 940 | 680 |
| RC81-000-01 | 1:1.923 | 540 | 74 | 100 | 1308 | 680 | 1038 |
| RC81-000-02 | 1:1.46 | 540 | 74 | 100 | 1308 | 896 | 788 |
| 75356-192 | 1:1.92 | 540 | 97 | 130 | 1715 | 893 | 1037 |
| 75356-146 | 1:1.46 | 540 | 97 | 130 | 1715 | 1175 | 788 |
| 74823-19 | 1:1.87 | 540 | 97 | 130 | 1715 | 918 | 1009 |
| 74823-14 | 1:1.39 | 540 | 97 | 130 | 1715 | 1235 | 750 |
| GT40U.B | 3:1 | 540 | 44 | 60 | 778 | 2334 | 180 |
| SF-100 | 1:1 | 540 | 15 | 20 | 265 | 265 | 540 |
| MCT-100A1 | 7.5:1 | 540 | 29.5 | 40 | 521 | 3912 | 72 |
| MCT-100A2 | 22.5:1 | 540 | 29.5 | 40 | 521 | 11738 | 24 |
| DCR1-0000 | 2.4:1 | 540 | 37 | 50 | 654 | 1570 | 225 |
|
US $50-110 / Piece | |
30 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Function: | Distribution Power, Clutch, Change Drive Torque, Change Drive Direction, Speed Changing, Speed Reduction, Speed Increase |
| Layout: | Cycloidal |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Horizontal Type |
| Step: | Four-Step |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| MODEL |
INPUT DATA | OUTPUT DATA | |||||
| Ratio | Maximum Rpm | KW | HP-CV | N.M | N.M | R.P.M | |
| AC78845A/B | 1:1.93 | 800 | 30 | 40 | 358 | 185 | 1544 |
| RC | 1:1.93 | 800 | 30 | 40 | 358 | 185 | 1544 |
| RC5/BB60X | 1:1.69 | 800 | 37 | 50 | 440 | 260 | 1352 |
| AC78846A/B | 1:1.93 | 540 | 55 | 75 | 972 | 504 | 1042 |
| 612619 | 1:1.93 | 540 | 74 | 100 | 1308 | 678 | 1042 |
| 612666 | 1:1.46 | 540 | 74 | 100 | 1308 | 896 | 680 |
| BB84X | 1:1.26 | 540 | 67 | 90 | 1184 | 940 | 680 |
| RC81-000-01 | 1:1.923 | 540 | 74 | 100 | 1308 | 680 | 1038 |
| RC81-000-02 | 1:1.46 | 540 | 74 | 100 | 1308 | 896 | 788 |
| 75356-192 | 1:1.92 | 540 | 97 | 130 | 1715 | 893 | 1037 |
| 75356-146 | 1:1.46 | 540 | 97 | 130 | 1715 | 1175 | 788 |
| 74823-19 | 1:1.87 | 540 | 97 | 130 | 1715 | 918 | 1009 |
| 74823-14 | 1:1.39 | 540 | 97 | 130 | 1715 | 1235 | 750 |
| GT40U.B | 3:1 | 540 | 44 | 60 | 778 | 2334 | 180 |
| SF-100 | 1:1 | 540 | 15 | 20 | 265 | 265 | 540 |
| MCT-100A1 | 7.5:1 | 540 | 29.5 | 40 | 521 | 3912 | 72 |
| MCT-100A2 | 22.5:1 | 540 | 29.5 | 40 | 521 | 11738 | 24 |
| DCR1-0000 | 2.4:1 | 540 | 37 | 50 | 654 | 1570 | 225 |
Key Market Insights Related to Worm Reduction Gearboxes
A gearbox is a mechanical device that allows you to shift between different speeds or gears. It does so by using one or more clutches. Some gearboxes are single-clutch, while others use two clutches. You can even find a gearbox with closed bladders. These are also known as dual clutches and can shift gears more quickly than other types. Performance cars are designed with these types of gearboxes.
Backlash measurement
Gearbox backlash is a common component that can cause noise or other problems in a car. In fact, the beats and sets of gears in a gearbox are often excited by the oscillations of the engine torque. Noise from gearboxes can be significant, particularly in secondary shafts that engage output gears with a differential ring. To measure backlash and other dimensional variations, an operator can periodically take the output shaft’s motion and compare it to a known value.
A comparator measures the angular displacement between two gears and displays the results. In one method, a secondary shaft is disengaged from the gearbox and a control gauge is attached to its end. A threaded pin is used to secure the differential crown to the secondary shaft. The output pinion is engaged with the differential ring with the aid of a control gauge. The angular displacement of the secondary shaft is then measured by using the dimensions of the output pinion.
Backlash measurements are important to ensure the smooth rotation of meshed gears. There are various types of backlash, which are classified according to the type of gear used. The first type is called circumferential backlash, which is the length of the pitch circle around which the gear rotates to make contact. The second type, angular backlash, is defined as the maximum angle of movement between two meshed gears, which allows the other gear to move when the other gear is stationary.
The backlash measurement for gearbox is one of the most important tests in the manufacturing process. It is a criterion of tightness or looseness in a gear set, and too much backlash can jam a gear set, causing it to interface on the weaker part of its gear teeth. When backlash is too tight, it can lead to gears jamming under thermal expansion. On the other hand, too much backlash is bad for performance.
Worm reduction gearboxes
Worm reduction gearboxes are used in the production of many different kinds of machines, including steel and power plants. They are also used extensively in the sugar and paper industries. The company is constantly aiming to improve their products and services to remain competitive in the global marketplace. The following is a summary of key market insights related to this type of gearbox. This report will help you make informed business decisions. Read on to learn more about the advantages of this type of gearbox.
Compared to conventional gear sets, worm reduction gearboxes have few disadvantages. Worm gear reducers are commonly available and manufacturers have standardized their mounting dimensions. There are no unique requirements for shaft length, height, and diameter. This makes them a very versatile piece of equipment. You can choose to use one or combine several worm gear reducers to fit your specific application. And because they have standardized ratios, you will not have to worry about matching up multiple gears and determining which ones fit.
One of the primary disadvantages of worm reduction gearboxes is their reduced efficiency. Worm reduction gearboxes usually have a maximum reduction ratio of five to sixty. The higher-performance hypoid gears have an output speed of around ten to twelve revolutions. In these cases, the reduced ratios are lower than those with conventional gearing. Worm reduction gearboxes are generally more efficient than hypoid gear sets, but they still have a low efficiency.
The worm reduction gearboxes have many advantages over traditional gearboxes. They are simple to maintain and can work in a range of different applications. Because of their reduced speed, they are perfect for conveyor belt systems.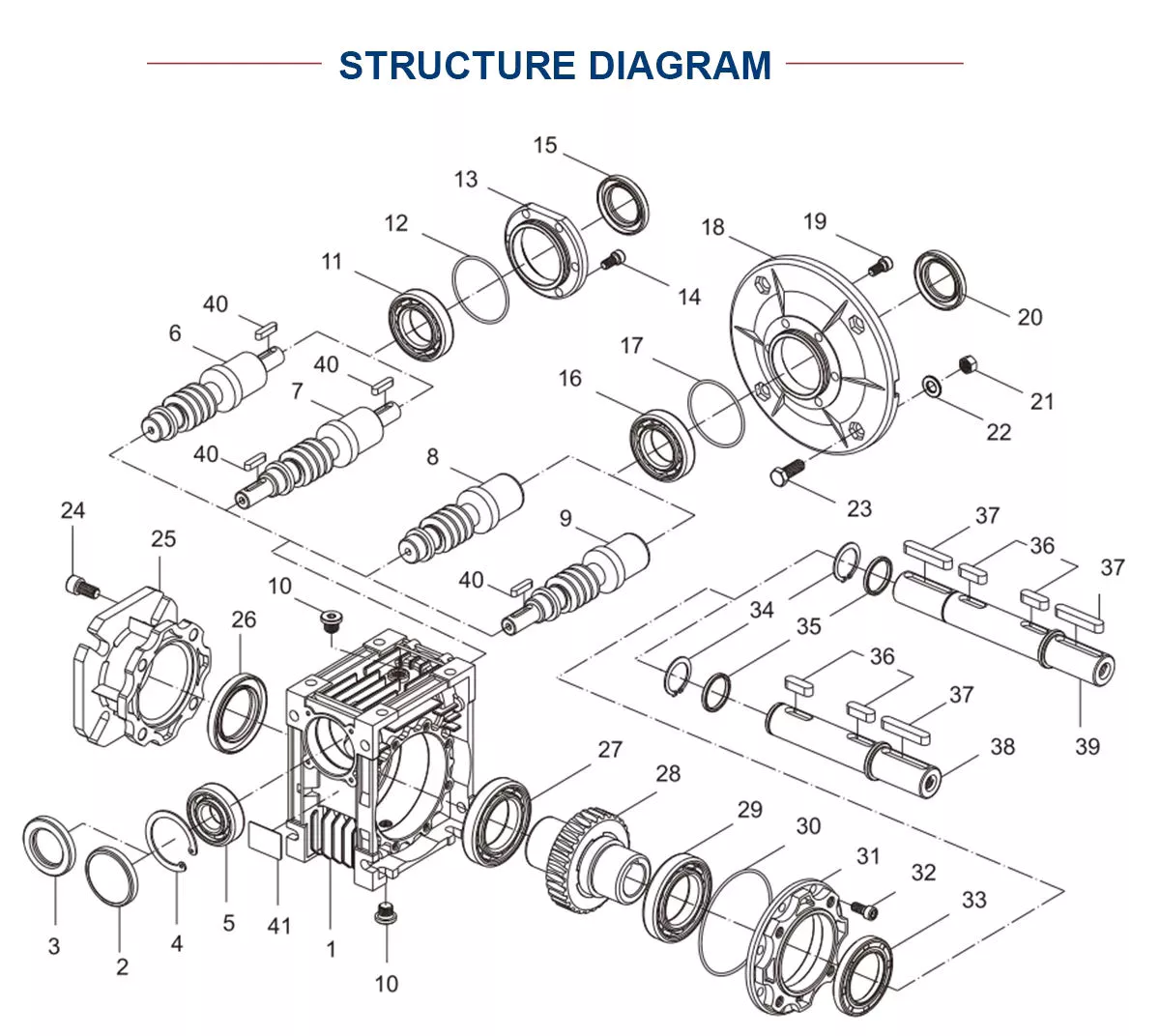
Worm reduction gearboxes with closed bladders
The worm and the gear mesh with each other in a combination of sliding and rolling movements. This sliding action is dominant at high reduction ratios, and the worm and gear are made of dissimilar metals, which results in friction and heat. This limits the efficiency of worm gears to around thirty to fifty percent. A softer material for the gear can be used to absorb shock loads during operation.
A normal gear changes its output independently once a sufficient load is applied. However, the backstop complicates the gear configuration. Worm gears require lubrication because of the sliding wear and friction introduced during movement. A common gear arrangement moves power at the peak load section of a tooth. The sliding happens at low speeds on either side of the apex and occurs at a low velocity.
Single-reduction gearboxes with closed bladders may not require a drain plug. The reservoir for a worm gear reducer is designed so that the gears are in constant contact with lubricant. However, the closed bladders will cause the worm gear to wear out more quickly, which can cause premature wear and increased energy consumption. In this case, the gears can be replaced.
Worm gears are commonly used for speed reduction applications. Unlike conventional gear sets, worm gears have higher reduction ratios. The number of gear teeth in the worm reduces the speed of a particular motor by a substantial amount. This makes worm gears an attractive option for hoisting applications. In addition to their increased efficiency, worm gears are compact and less prone to mechanical failure.
Shaft arrangement of a gearbox
The ray-diagram of a gearbox shows the arrangement of gears in the various shafts of the transmission. It also shows how the transmission produces different output speeds from a single speed. The ratios that represent the speed of the spindle are called the step ratio and the progression. A French engineer named Charles Renard introduced five basic series of gearbox speeds. The first series is the gear ratio and the second series is the reverse gear ratio.
The layout of the gear axle system in a gearbox relates to its speed ratio. In general, the speed ratio and the centre distance are coupled by the gear axles to form an efficient transmission. Other factors that may affect the layout of the gear axles include space constraints, the axial dimension, and the stressed equilibrium. In October 2009, the inventors of a manual transmission disclosed the invention as No. 2. These gears can be used to realize accurate gear ratios.
The input shaft 4 in the gear housing 16 is arranged radially with the gearbox output shaft. It drives the lubricating oil pump 2. The pump draws oil from a filter and container 21. It then delivers the lubricating oil into the rotation chamber 3. The chamber extends along the longitudinal direction of the gearbox input shaft 4, and it expands to its maximum diameter. The chamber is relatively large, due to a detent 43.
Different configurations of gearboxes are based on their mounting. The mounting of gearboxes to the driven equipment dictates the arrangement of shafts in the gearbox. In certain cases, space constraints also affect the shaft arrangement. This is the reason why the input shaft in a gearbox may be offset horizontally or vertically. However, the input shaft is hollow, so that it can be connected to lead through lines or clamping sets.
Mounting of a gearbox
In the mathematical model of a gearbox, the mounting is defined as the relationship between the input and output shafts. This is also known as the Rotational Mount. It is one of the most popular types of models used for drivetrain simulation. This model is a simplified form of the rotational mount, which can be used in a reduced drivetrain model with physical parameters. The parameters that define the rotational mount are the TaiOut and TaiIn of the input and output shaft. The Rotational Mount is used to model torques between these two shafts.
The proper mounting of a gearbox is crucial for the performance of the machine. If the gearbox is not aligned properly, it may result in excessive stress and wear. It may also result in malfunctioning of the associated device. Improper mounting also increases the chances of the gearbox overheating or failing to transfer torque. It is essential to ensure that you check the mounting tolerance of a gearbox before installing it in a vehicle.


editor by czh 2022-11-28









